Author: Jordan Physiotherapist
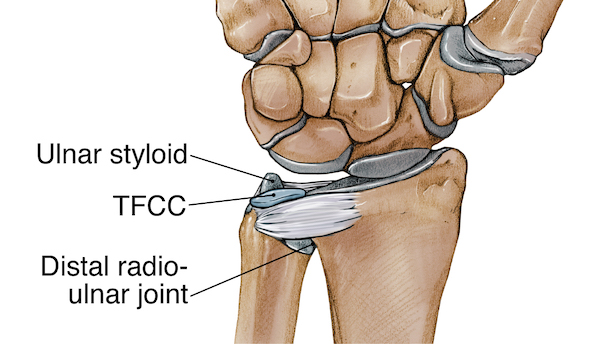
What is a Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex(TFCC)Injury? The TFCC is a load bearing structure that sits at the bottom of your wrist on the pinky side of your hand. Its role is to act as a stabiliser for the pinky side of the wrist [1]. When injured, this can cause your wrist to become unstable after some wrist fractures[1]. One study showed that 96.5% of some wrist fractures also have TFCC injuries[2].
Now that we know what the TFCC is, what does it feel like? A TFCC injury will cause you to feel a sharp pain on the pinky side of the wrist that increases with activity. You can also experience swelling, clicking and popping noises, difficulty gripping and holding onto objects, feeling that your wrist is unstable, and if you have a wrist fracture and complete TFCC tear, you may notice a pronounced bump on th epinky side of your wrist [1].
What can cause a TFCC injury? In addition to the previously mentioned wrist fracture, there are many other ways one may damage the TFCC. Other causes may include gymnastics, falling, hitting a volleyball, swinging a bat or racket and using vibrating power tools, as these activities all increase the load on the TFCC [3]. ATFCC injury may also be caused due to aging as a result of your wrist ligaments becoming weaker[3].
So, how can I be sure if I have a TFCC injury? If you think you may have injured your TFCC, a Physiotherapist can perform physical tests to confirm the diagnosis. Your Physio may send you for an X-Ray or refer for an MRI if a better picture is needed. A referral to an Orthopaedic Specialist may be required in some cases [1].
And what can be done? TFCC injuries are always managed by a Physiotherapist–even if surgery is need. Your physio will provide a combination of hands-on techniques, strengthening exercises and stretches to help improve your wrist movement and strength to decrease your pain[1]. Treatment will be tailored to your specific needs–whether that is for someone who wishes to resume their day-to-day activities pain free all the way to athletes who wish to return to their respective sport. If you have or suspect you have injured your TFCC, book in an appointment to see one of our Physiotherapists today!
References: 1.Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injuries. (n.d.). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Triangular_Fibrocartilage_Complex_Injuries2. Yan B, Xu Z, Chen Y, Yin W. Prevalence of triangular fibrocartilage complex injuries in patients with distal radius fractures: a 3.0T magnetic resonance imaging study. J Int Med Res. 2019 Aug; 47(8):3648-3655. doi: 10.1177/0300060519856157. Epub 2019 Jun 24. PMID: 31234678; PMCID: PMC6726770.3. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics. Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex.http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/triangular_fibrocartilage_complex
